As people become increasingly health-conscious, it’s clear that the nutrients in our everyday diets are often insufficient. This has led to a surge in products designed to fill the gap with nutritional supplements. According to FDL Digital Nutrition Advocacy, minerals now account for one of the largest segments in the health food industry.
But with so many mineral supplements on the market, the big question is:
Can our bodies actually absorb and use them effectively?

This is where the concept of “chelation” comes in. Chelation is a breakthrough solution that not only improves absorption but is also gentler on the digestive system.
Chelated Mineral Salts: The Key to Enhanced Absorption and Bioavailability
Chelated mineral salts are formed through the reaction of minerals with amino acids, such as glycine, creating a unique “chelated” structure. This specialized structure significantly improves the stability and absorption of minerals.
The term “chelation” originates from the Greek word chele, meaning “claw,” vividly illustrating how amino acids “grasp” the minerals and shield them from degradation caused by external factors like stomach acid.
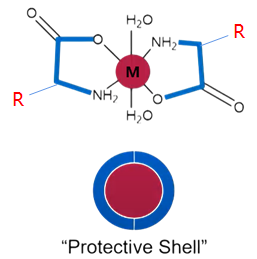
When chelated mineral salts enter the gastrointestinal tract, the ring-like structure formed by amino acids ensures the stability of the minerals, preventing them from being degraded by digestive enzymes in gastric fluids. This process reduces irritation to the stomach lining, alleviating discomfort such as stomach pain.
Once the chelate reaches the jejunum (a part of the small intestine), the amino acid structure is broken down, releasing mineral ions. At this stage, the minerals can pass through the intestinal wall into the bloodstream, where they are efficiently absorbed and utilized by various organs in the body.
Compared to traditional inorganic mineral salts, chelated mineral salts offer significantly higher bioavailability—meaning they are easier for the body to absorb and utilize. This higher efficiency allows consumers to achieve the same absorption results with a lower daily dose of chelated mineral supplements, offering unparalleled convenience and benefits.
Over 200 clinical studies have now confirmed that chelated mineral salts offer significantly higher absorption and bioavailability. For example, clinical research has shown that magnesium glycinate, a chelated form of magnesium, has a bioavailability up to five times greater than that of inorganic mineral salts.
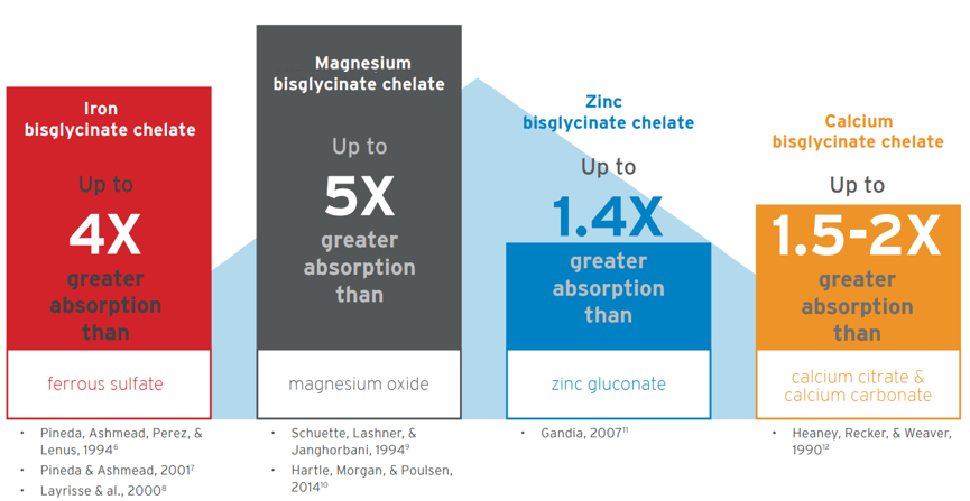
This remarkable efficiency highlights the potential of chelated mineral salts as a highly effective option for mineral supplementation.
Rising Global Demand: The Bright Future of Chelated Mineral Salts
Market reports indicate that the global chelated mineral salts market is poised for substantial growth over the next decade. The market size is projected to increase from $1.1 billion in 2022 to $2.1 billion, marking an impressive surge.
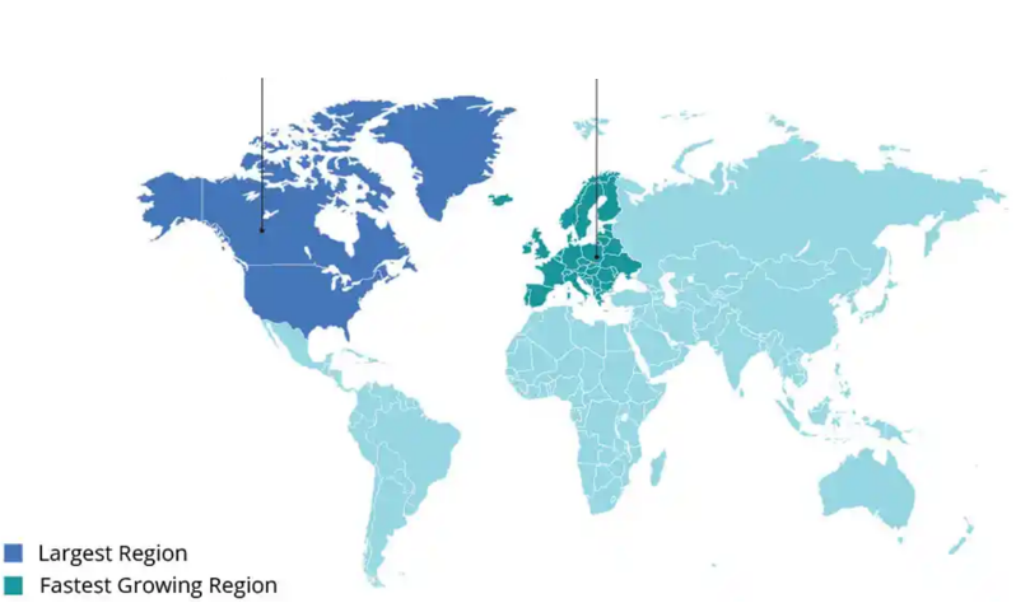
The chelated mineral salts market is expected to maintain robust growth, with North America and Europe leading the charge. North America currently holds the title of the largest market globally, while Europe is emerging as the fastest-growing region.
This strong performance in key markets underscores the increasing global demand for high-quality mineral supplementation solutions.
Chelated mineral salt products have experienced explosive growth on e-commerce platforms like Amazon. Over the past year, sales on Amazon’s U.S. platform alone generated an impressive revenue of 121 million USD from chelated mineral salt-related products.
This striking trend underscores the rapidly increasing consumer demand for chelated mineral supplements, solidifying their position as a go-to solution for enhanced nutrition.
Pure-Chel™ Chelated Mineral Salts: Your Premier Choice for High Quality, Purity, and Stability
As global health awareness grows, the market for chelated mineral salts is poised for remarkable expansion. Richen leads the way with its innovative approach, using premium glycine as the ligand for its chelated mineral salts. This ensures superior mineral stability and optimal absorption efficiency.
Premium Mineral Sources
Richen Nutritionals secures high-quality mineral sources and leverages advanced mineral nutrition technology to offer a safe, comprehensive, and consistently reliable product line. In addition, Richen provides tailored application solutions to meet the specific needs of its global customers.

High Purity
Chelated mineral salts are typically produced using either spray-drying or crystallization methods. Pure-Chel™ utilizes a proprietary crystallization process, optimizing solubility, lattice formation, and crystallization controls. This cutting-edge method ensures efficient separation of minerals from impurities, delivering a superiorly pure mineral product that meets the highest quality standards.
100% Fully Chelated
Through proprietary testing methodologies, Richen guarantees that Pure-Chel™ chelated mineral salts are fully chelated. This complete chelation results in a highly stable structure with enhanced absorption and bioavailability. Fully chelated minerals are easier for the body to absorb, increasing their effectiveness and addressing absorption challenges for elderly, children, and individuals with gastrointestinal conditions.
Optimized for Versatile Applications
Richen’s advanced application technologies offer innovative solutions tailored to diverse dietary supplement formats. Pure-Chel™ chelated mineral salts are engineered with optimized particle size, bulk density, and flowability to meet the precise demands of various supplement forms, ensuring seamless integration into different product formulations.
Richen Nutritionals is dedicated to helping people achieve their health goals, focusing on key market areas such as elderly nutrition, early nutrition, brain health, bone health, and oral beauty. Richen Nutritionals consistently delivers reliable, science-based nutritional solutions along with warm, timely, and professional service.
Reference:
[1] Pineda O, Wayne Ashmead H D, Perez J M, et al. Effectiveness of iron amino acid chelate on the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in adolescents[J]. Journal of Applied Nutrition, 1994, 46(1): 2-13.
[2] Coplin M, Schuette S, Leichtmann G, Lashner B. Tolerability of iron: a comparison of bisglycino iron II and ferrous sulfate. Clin Ther. 1991 Sep-Oct;13(5):606-12.
[3] Hartle, J. W. et al. “Development of a Model for In‐Vitro Comparative Absorption of Magnesium from Five Magnesium Sources Commonly Used as Dietary Supplements.” The FASEB Journal 30 (2016): n. pag.